Pregnancy, a miraculous journey that brings new life into the world, is a topic of fascination and curiosity. While the experience of pregnancy is unique for each individual, one common question arises: What is the average length of a human pregnancy, and is it influenced by various factors? In this article, we will explore the duration of human pregnancies, the factors that can affect it, and the significance of understanding this period.
Contents
- 1 Understanding Human Pregnancy Length
- 2 Factors Influencing Pregnancy Duration
- 3 Predicting Due Dates
- 4 The Role of Medical Interventions
- 5 Long and Short Pregnancy Concerns
- 6 Preparing for the Arrival
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 FAQs
- 8.1 1. Can a pregnancy last longer than 42 weeks?
- 8.2 2. Are there ways to naturally induce labor if a pregnancy goes overdue?
- 8.3 3. What are the risks associated with preterm birth?
- 8.4 4. Can genetics really influence the timing of labor?
- 8.5 5. How can a pregnant woman ensure a healthy pregnancy and full-term delivery?
Understanding Human Pregnancy Length
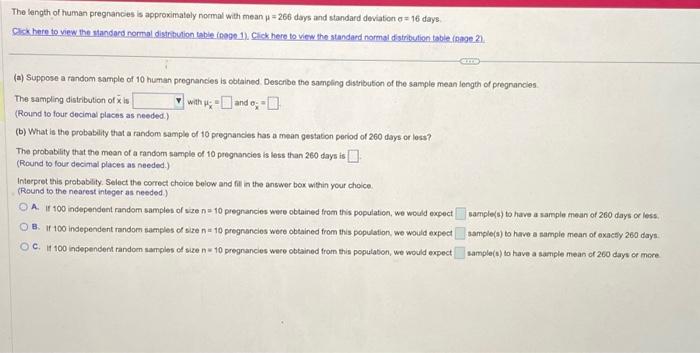
Human pregnancies are approximately normal in length, with an average duration of around 40 weeks, or 280 days. This standard duration allows for the development of a healthy, full-term baby. However, it’s crucial to note that not all pregnancies adhere strictly to this timeline. Some may last longer, while others conclude a bit earlier.
Factors Influencing Pregnancy Duration
The Role of Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in determining the length of a pregnancy. If a woman has a family history of shorter or longer pregnancies, there’s a chance she may follow the same pattern. Genes can influence the timing of labor, the mother’s ability to maintain pregnancy, and the baby’s growth.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also influence pregnancy length. Exposure to toxins, pollution, and stress may contribute to preterm births. On the contrary, a healthy and stress-free environment can support a full-term pregnancy.
Maternal Health and Pregnancy Length
A mother’s overall health is a critical factor in pregnancy duration. Women with chronic health conditions or those who experience complications during pregnancy may deliver earlier. Conversely, mothers who maintain good health throughout their pregnancy are more likely to carry their baby to full term.
The Importance of Prenatal Care
Regular prenatal care is essential to monitor the progress of the pregnancy and address any potential issues that may arise. Medical professionals can provide guidance on nutrition, lifestyle, and overall health to support a healthy, full-term pregnancy.
Predicting Due Dates
Estimating a due date is a common practice in prenatal care. Healthcare providers use several methods, including the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP), ultrasound measurements, and physical examinations. These estimations help ensure that the baby is born at a safe and healthy stage of development.
The Role of Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to ensure a safe pregnancy and delivery. Inducing labor or scheduling a cesarean section may be recommended if there are concerns about the health of the mother or baby.
Long and Short Pregnancy Concerns
Risks Associated with Preterm Births
Preterm births, which occur before 37 weeks of gestation, can pose health risks to the baby. These infants may have underdeveloped organs and require specialized care in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
Risks Associated with Post-term Pregnancies
Pregnancies that extend beyond 42 weeks are considered post-term. While these cases are relatively rare, they can lead to complications, such as decreased amniotic fluid or an increased risk of stillbirth. Medical professionals closely monitor post-term pregnancies.
Preparing for the Arrival
As the due date approaches, expectant parents should prepare for the arrival of their newborn. This includes packing a hospital bag, setting up the nursery, and finalizing birthing plans. Being well-prepared can help reduce stress and ensure a smooth transition into parenthood.
Conclusion
The length of human pregnancies is indeed approximately normal, with an average duration of 40 weeks. However, various factors can influence this timeline, making it crucial for expectant parents to stay informed and seek proper prenatal care. Understanding the factors that affect pregnancy length can contribute to a healthier and safer childbirth experience.
FAQs
1. Can a pregnancy last longer than 42 weeks?
Yes, although it’s rare, some pregnancies can extend beyond 42 weeks. These are considered post-term pregnancies and require close monitoring.
2. Are there ways to naturally induce labor if a pregnancy goes overdue?
While there are natural methods like walking and consuming certain foods, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before attempting to induce labor.
3. What are the risks associated with preterm birth?
Preterm babies may face health complications, including underdeveloped organs, breathing difficulties, and the need for neonatal intensive care.
4. Can genetics really influence the timing of labor?
Yes, genetics can play a role in when labor starts and how long a pregnancy lasts, as it can affect a woman’s hormonal responses.
5. How can a pregnant woman ensure a healthy pregnancy and full-term delivery?
Regular prenatal care, a balanced diet, adequate rest, and stress management are essential for a healthy pregnancy and full-term delivery.